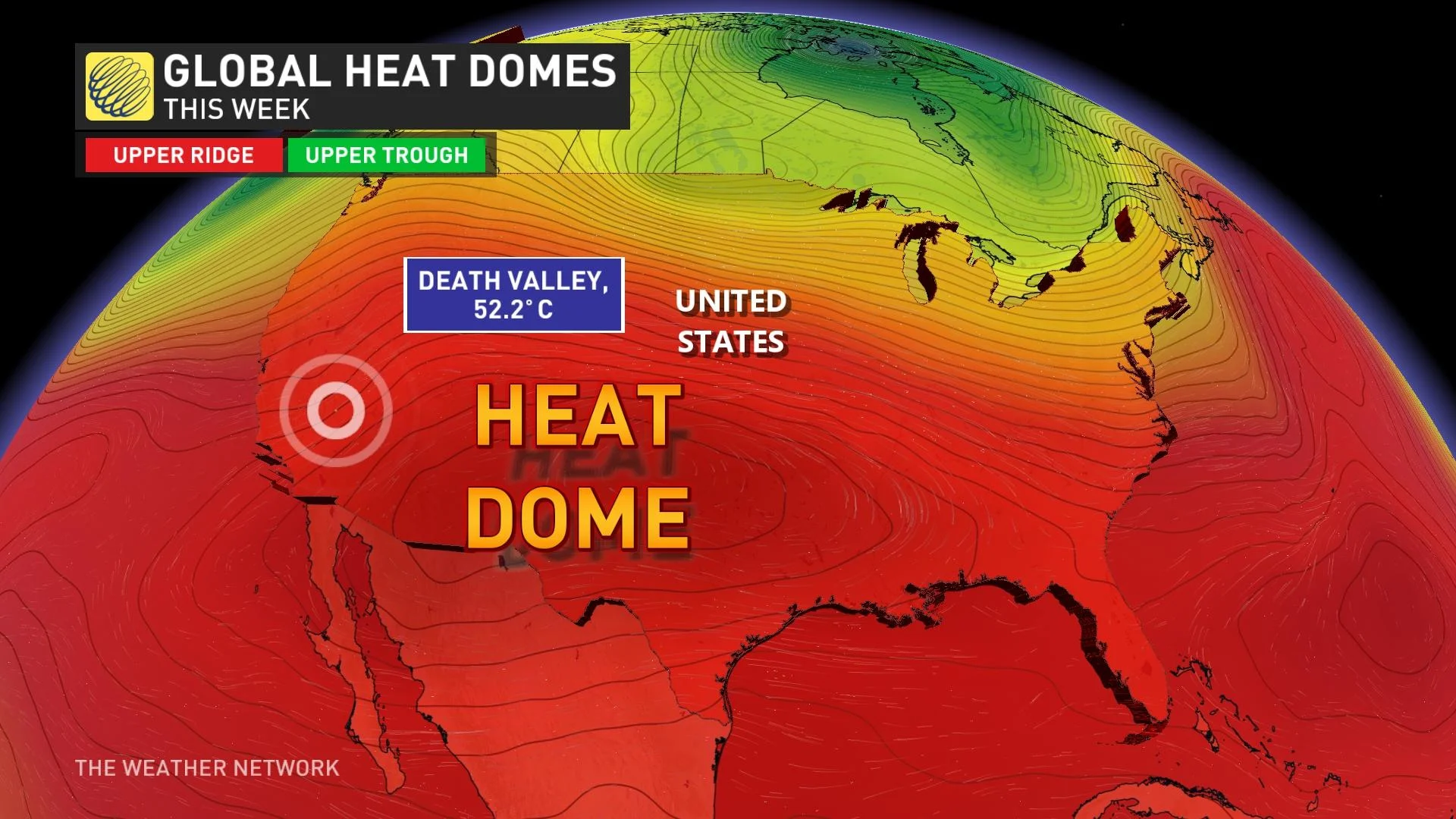
Similar to the frequency and intensity of atmospheric rivers in 2021, heat domes are now assuming crucial roles in precipitating extreme weather events in 2023, particularly in recent weeks.
Currently, the Northern Hemisphere is experiencing four distinct heat domes, leading to perilously high temperatures that have shattered numerous noteworthy records.
Over the past two weeks, a heat dome has exerted significant effects on the southwestern United States, particularly in North America.
In the city of Phoenix, Arizona, a new all-time record has been set, with temperatures reaching 43.3°C or higher for an astounding 19 consecutive days, spanning from June 30 to July 18. Unfortunately, the scorching conditions are far from over, as weather forecasts predict daytime temperatures to persist above 43.3°C for the next seven to 10 days.
Record-breaking temperatures have been observed in the North Atlantic Ocean. The heat surge can be attributed to several factors, such as reduced wind activity, which accelerates surface warming with minimal upwelling. Additionally, the scarcity of Saharan dust reduces the amount of light reflected back to space, exacerbating the warming, along with the underlying influence of climate change.
Although the heat dome’s impact on land has been limited, it did facilitate the arrival of hot and humid weather conditions to Newfoundland, making its presence felt in the region.
A different heat dome situated above North Africa has resulted in a series of record-breaking events across Europe. The countries most severely affected by this phenomenon include Spain, Italy, Morocco, and Algeria. For instance, on a recent Tuesday, Rome registered a scorching temperature of 42.9°C, setting a new record as the highest reading ever recorded in the city’s history.
The scorching heat wave has been engulfing southern Europe during its peak summer tourist season, causing record-breaking temperatures, notably in Rome, and prompting authorities to issue warnings about the heightened risk of fatalities.
During the summer in the Northern Hemisphere, it is not unusual for this part of the world to experience hot weather. The presence of ridges responsible for these heat domes is a customary atmospheric configuration, but their intensity this year is remarkable.
Moreover, the prolonged duration of these heat episodes also contributes to the phenomenon’s impact. For instance, the southwestern United States has been enduring exceptionally high temperatures for several weeks. Under the heat dome, the atmosphere becomes stagnant, allowing the heat to accumulate and intensify.